(14) Greek civilization, language, and literature.
After adopting Phoenician graphic-alphabet in 900 BC
they employed a vowel system and added six more letters
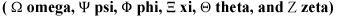 to make it a 24 letter alphabet.
Earlier, to make it a 24 letter alphabet.
Earlier,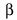 was pronounced as ‘b.’ Now in
Modern Greek it is pronounced as ‘v.’ It took a long time to develop the
letters. There were many Greek dialects and there were certain differences
in their style of writing. Lastly the Ionian style of lettering was
adopted in general and after 400 BC the letters became uniform. The
literature and art flourished mainly in the Classical Greek period. was pronounced as ‘b.’ Now in
Modern Greek it is pronounced as ‘v.’ It took a long time to develop the
letters. There were many Greek dialects and there were certain differences
in their style of writing. Lastly the Ionian style of lettering was
adopted in general and after 400 BC the letters became uniform. The
literature and art flourished mainly in the Classical Greek period.
Phonology. Although the dialects of Greek were
mutually intelligible within a normal limit of understanding but the
pronunciations of words and accents differed from period to period and
from dialect to dialect. The short and long sounds of vowels also varied
in different dialects and the political situations in the country also
brought many changes with the intermigration of the dialects. But,
during the establishment of Alexander’s empire in the 4th century BC and
after the breakdown of old political barriers, a uniformity took place in
the spoken language. This form of language was called the Koine (means
the common language) or Hellenistic Greek (400 BC - 600 AD). It replaced
the other dialects and the speaking and writing systems were much
standardized.
Grammar also changed in different periods. A change
of language is noticed in the writings of Plato and Demosthenes. The
spoken language still kept on changing even during the period of Byzantine
empire (500-1500 AD) and the written language kept on improving which
created a big rift between the local vernacular and the literary Greek.
This situation gave birth to a separate kind of ‘Demotic’ language of
general everyday use.
All the major phonological and grammatical changes
which are seen between Koine and the Modern Greek mostly
happened within this period. Earlier there were three numbers for
pronouns and verbs, singular, dual and plural. Then ‘dual’ was dropped
and, only singular and plural were left.
From Ancient Greek to Modern Greek the formation of
many words were also changed. For example: The ancient Greek word pente
(five) became pende, hepta and okto (seven and eight)
became efta and okhto, paidia (boys) became pedhya
and so on. There were also semantic changes in certain words, just as: the
word alogho which previously meant ‘irrational,’ later it
meant ‘horse;’ skiazome which previously meant ‘I am in
shadow,’ later it meant ‘I fear.’
The vocabulary of Greek language consists of
local collections and borrowings. Considering the origin of Greek, there
were many Mycenaean words in 2nd millennium BC whose original form
corresponded to certain Greek words like leon (lion), onos
(ass), elephas (ivory) etc.
By using preverbs, by forming compounds and by
adding prefixes or suffixes to these prime words they enriched their
vocabulary. Later on they also borrowed a considerable number of words
from other sources, such as, Italian, Turkish, French and also Latin.
Culture and literature of Greece.
Greece was the origin of western civilization that
started about 3,000 years ago. The peak of its glory was around 500 BC
which was the golden age for Athens. Democritus, Socrates and his disciple
Plato were in the 5th century BC and Aristotle was in the 4th century BC.
Democritus introduced the theory of the creation of the universe
with the atoms; Socrates told about the general universal
principles and about one Divinity (but he was sentenced to death by
drinking poison for telling the truth which they called unorthodox);
Plato believed in the immortality of the soul and introduced his
reasonings based on his idea of the intellect part of the being and the
desire part of the being. He started a school of philosophy in Athens
called “Academy.” His pupil Aristotle explained in his theory of
physics about the constant change in every form, phase and aspect of
creation which is the inherent nature of this world, but only God is
unchanged and eternal. He used the word theology for the philosophy
of God.
The two fiction stories the Iliad and the Odyssey
written in a long poetry form are famous which are traditionally believed
to be composed by a blind but imaginative bard, Homer (alone or together
with his traveling friend), around 700 BC and were recited in the
community. Between 300 and 100 BC from the available handwritten parts of
the Iliad and the Odyssey and from the prevailing recited stories, the
existing books that are available nowadays, were compiled, edited and
again properly written.
The Iliad and the Odyssey of Homer.
The Iliad is a fancied description of the last
part of the legendary Trojan war (in twenty-four small sections) that went
on for 10 years (around 1350 BC) between the Greek army and the king of
Troy to rescue Helen (the Queen of Sparta) who was abducted by the son of
the king of Troy. The characters of the story are fictitious and the plot
of the story follows the imagination of the writer. The story ends with
Hector’s funeral who was leading the Greek forces in the end.
The Odyssey is also in the ancient style of
Greek poetry that describes the adventures of King Odysseus (the main
character of the fiction story) in a heroic way when he is returning back
to his home after fighting a battle. The story also portrays the lust,
jealousy and the revengefulness of the gods who were produced by the
imagination of Homer and which became the guidelines for portraying the
gods of the Greek mythology.
The story starts from the middle, where, after seven
years of captivation by a sea nymph, the hero of the play, Odysseus, gains
the favor of the chief god Zeus and goddess Athena and, with the help of
Hermes, he comes out of the captivity and sails forward in a raft. But,
the god of the sea, Poseidon, ragefully capsizes the raft by causing a sea
storm because he had killed one of his demon friends on one of the islands
where he stayed during his journey. He was washed ashore by the waves when
a princess finds him and takes him to her homeland.
Prior to those happenings he went through a number of
adventures that happened in various imaginary lands that were inhabited
with people having magic powers and also there were some demons on certain
islands. Once when he landed on an island the lady enchantress of that
island made his people pigs and Odysseus her lover. With her help he
visits the underworld where he sees ghosts of his mother and the people
who died in war. Later on as he proceeds with his men towards his country,
the god’s rage in the form of a violent thunderbolt destroys the ship
along with his people because some of his men had stealthily eaten the
cattle of the sun god on one of the islands. He is washed ashore on the
island of Ogygia, the land of the sea nymph, from where the story started.
Finally he comes home after ten years of tragic life and joins his wife.
Such stories give an idea of the society and the people
of those days and also their beliefs. It is a fact that the ancient Greeks
laid the foundation of western civilization. They also contributed to the
knowledge of biology, geometry, history, philosophy, physics and the
logics of Plato, fine arts, architecture and music. The temple of Athena
(450 BC) is famous for its architecture.
The golden age of Athens began to decline when the
Peloponnesian war broke out in 431 BC and shortly after that the epidemic
of plague killed one third of the Athenians, but, during the reign of
Alexander it again regained its prosperity. However, the expanding
powerful conquests of the Roman Empire took over Macedonia (Greece) in 148
BC and there were lots of disturbances and destructions in Greece during
that time.
The origin of Homer’s mythological imaginations and the religion of
Greece.
In ancient times there were trade connections between
the eastern Mediterranean countries, Persia and India, and also people
traveled long distances in those days. Thus, the social culture of India
and certain popular stories of the Puranas,
 like: the creation of celestial and
material world by Brahma, first material sky then the earth; the first
originators of human civilization Manu and Shatroopa; wars between gods
and demons in the celestial plane; the story of water deluge that flooded
the whole world (dissolving the celestial abodes also) when Rishi
Satyavrat kept the subtle bodies of all the souls with him and stayed in
the ship during the previous kalp pralaya; the story of gods and
goddesses when they went to Vishnu’s abode and there they heard a Divine
voice; and the stories of god Indra, Varun, Kamdeo, Kuber, Agni, Vayu and
the creator Brahma etc. traveled through sea routes. Also, many other
commonly known stories of the Indian community reached these countries by
word of mouth with some additions and subtractions as they traveled from
mouth to mouth and the people of these countries incorporated them in
their mythologies. like: the creation of celestial and
material world by Brahma, first material sky then the earth; the first
originators of human civilization Manu and Shatroopa; wars between gods
and demons in the celestial plane; the story of water deluge that flooded
the whole world (dissolving the celestial abodes also) when Rishi
Satyavrat kept the subtle bodies of all the souls with him and stayed in
the ship during the previous kalp pralaya; the story of gods and
goddesses when they went to Vishnu’s abode and there they heard a Divine
voice; and the stories of god Indra, Varun, Kamdeo, Kuber, Agni, Vayu and
the creator Brahma etc. traveled through sea routes. Also, many other
commonly known stories of the Indian community reached these countries by
word of mouth with some additions and subtractions as they traveled from
mouth to mouth and the people of these countries incorporated them in
their mythologies.
For example: the story of water deluge (pralaya)
became ‘the great flood’ of the Bible, and the stories and the epithets of
our celestial gods and goddesses became the source of their imagination
about mythologizing the characters of gods and goddesses in their religion
and worship. Thus, we find that Assyrians, Babylonians, Sumerians,
Semites, Egyptians and Greeks, all of them believed and worshipped many
gods and goddesses with somewhat similar characters like god of rain and
storm (Zeus), god of love (Eros), god of underworld (Hades), goddess of fire
(Hestia), and goddess of wisdom (Athena), etc. Zeus was their chief god. In addition to that they also created many more gods and
goddesses with their own imaginations. The forms and features of their
gods and goddesses were created either in a human form or a combination of
human and animal form (as Egyptian gods), whatever befitted according to
their nature, imagination and social living.
We find that the ancient society of Greece had adopted
certain social customs that were prevailing in India. Such as: the
husband headed the family and the wife ran the household affairs; parents
arranged and decided their children’s marriage; a girl was controlled and
protected by her parents before marriage and by her husband after
marriage; and many more such customs.
|